top of page


Saginaw Coun†y Weather
Weather for your area and All of Michigan

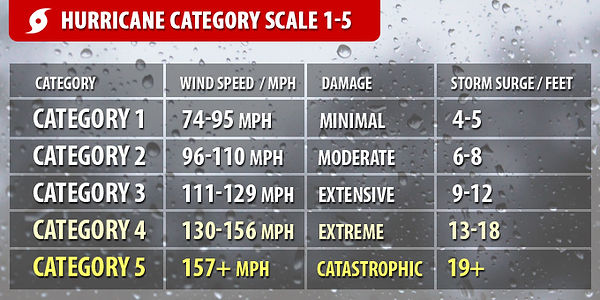
The Atlantic Hurricane Season is from June 1 - November 30
A hurricane is a tropical cyclone, which generally forms in the tropics and is accompanied by thunderstorms and a counterclockwise circulation of winds. Tropical cyclones are classified as follows:
Tropical Depression:
Organized system of clouds and thunderstorms with defined surface circulation and max sustained winds of 38 mph or less.
Tropical Storm:
Organized system of strong thunderstorms with a defined surface circulation and maximum sustained winds of 39-73 mph.
Hurricane:
Intense tropical weather system of strong thunderstorms with a well-defined surface circulation & max sustained winds of 74 mph or higher.
Storm Surge:
Water that is pushed toward the shore by the force of the winds swirling around the storm. This advancing surge combines with the normal tides to create the hurricane storm tide, which can increase the mean water level 15 feet or more.
Inland Flooding:
In the last 30 years, inland flooding has been responsible for more than half the deaths associated with tropical cyclones in the US.
High Winds:
Hurricane force winds can destroy poorly constructed buildings and mobile homes. Debris such as signs, roofing material, and small items left outside become flying missiles in hurricanes.
Tornadoes:
Hurricanes can produce tornadoes that add to the storm's destructive power. They are most likely to occur in the right-front quadrant of the hurricane.
bottom of page